What is Microsoft OneDrive and how does it work for SMBs?
by Jon Lober | NOC Technology
Microsoft OneDrive. A primer for small business.
Most of Microsoft’s products are instantly familiar, regardless of the last time that you used one. Although Windows, Word, Excel, and Outlook have all improved substantially over the past twenty years, someone who has not used one of the programs since Y2K would not be lost if they were to suddenly return to the latest Microsoft Office version.
That is, until they go to save their document.
For many small business owners and employees, Microsoft OneDrive has become an irreplaceable part of their workflow. For many others, it remains a baffling option that lives in their File Explorer—only raising its head when they go to save a document.
SMEs that use Microsoft’s business software and platform have much to gain by embracing the OneDrive, but it is hard to embrace what you do not understand.
What is Microsoft OneDrive?
OneDrive is Microsoft’s cloud service solution for individuals, businesses, schools, and organizations that want to store their data remotely. Cloud services like OneDrive allow organizations to store their information in a centralized location that anyone (with permission) can access from anywhere. (Click to learn more from NOC about what the cloud is and how it works.)
Microsoft launched its first cloud storage system in 2007. Over the past sixteen years, that product has evolved into an entire family of cloud-hosted offerings that includes OneDrive, SharePoint, and Microsoft 365. Most SMB owners and employees know OneDrive in its business-focused form—"OneDrive for work or school.” Formerly known as “OneDrive for Business,” some users may still encounter OneDrive under this name.
What can you do with OneDrive?
OneDrive allows users to sync, store, and backup their files in the Microsoft cloud.
For most SMEs, cloud storage is more flexible, has greater capacity, and provides greater data security compared to locally-stored files. OneDrive also allows everyone on a team to work on the same files, from the same folder. Users that combine OneDrive with Microsoft 365 can even collaborate on the same document in real time. This eliminates the need for multiple versions of a document or frustrating duplicated efforts.
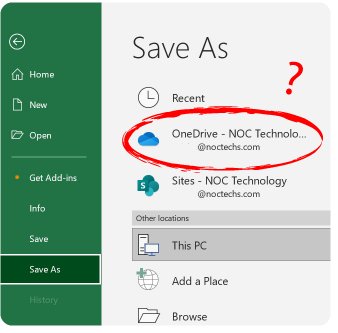
Most users interact with OneDrive in their File Explorer, where it appears as an option in the left-hand navigation pane.
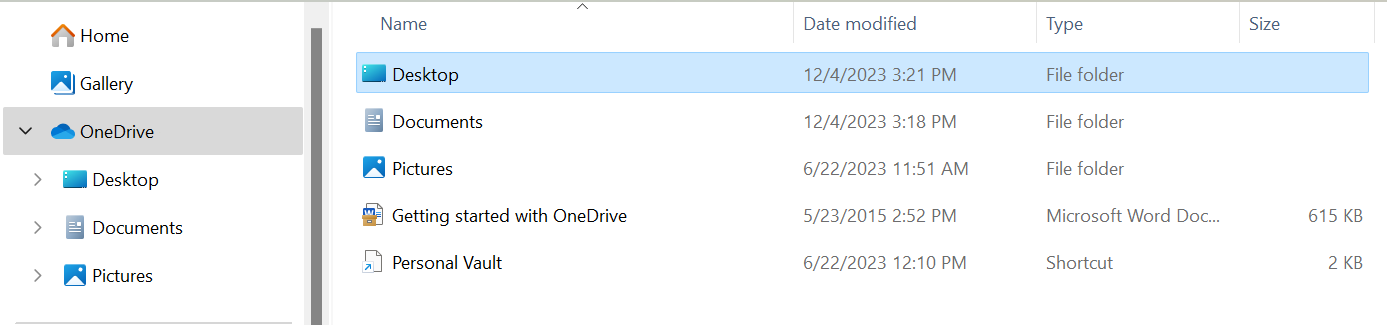
In File Explorer, you can drag and drop files into OneDrive or open a file just like with any other folder. If you are working on a document in any Office program, OneDrive appears as an option under “Save As” along with other familiar, locally-available locations. (Click to learn how to save and share Microsoft Office Files in One Drive.)
Any file that you save, delete, or modify in a OneDrive folder has that change automatically echoed in the cloud, a process known as “syncing.” However, in order to access those files, users must be connected to the internet. This saves space on a user’s computer. (Users that want to be able to access their files offline can also configure OneDrive to allow offline access.)
OneDrive also provides backup options to users, which means that OneDrive can automatically store a copy of selected folders (or your entire computer) on an ongoing basis. Robust backup is extremely important for small businesses, since it can eliminate the risk of data loss associated with damaged, lost, or stolen computers.

When you save a file to OneDrive, where are you saving it?
When you save a Microsoft Office file (or any other file) to OneDrive, that data is stored on a remote server, which your computer accesses through an internet connection. Unlike the other files on your desktop and hard drive (known as local files), OneDrive files are physically stored in a separate geographic location.
Specifically, Microsoft stores all OneDrive and SharePoint files in one of its 160 Azure data centers, which are separated into
60 geographic regions around the world. Most users
in the United States will have their data stored in one the ten Microsoft Azure data centers located in Iowa, Virginia, Georgia, Illinois, Texas, Wyoming, California, Washington, Arizona, or (soon) Georgia. Although the physical location of the data center does not matter to many small business owners, some may need to know in order to comply with data security or data residency regulations.
In order to protect users , OneDrive always saves two copies of every file—one primary and one secondary—in two distinct geographic regions, providing an additional layer of backup. This protocol prevents accidental data loss that could caused by a catastrophic event at a data center, such as a fire, earthquake, hurricane, or other natural disaster.







